Money Management(Student)
Money management is a crucial skill that students must learn to navigate successfully through their academic and future professional lives. This guide explores the sources of money, its principal uses, the pitfalls of mismanagement, the benefits of good management, and the importance of saving. By understanding these aspects, students can develop financial literacy and make informed decisions about their finances.
Sources of Money
1. Allowances
For many students, allowances from parents or guardians are the primary source of money. These regular payments are intended to cover basic needs, such as food, transportation, and school supplies.
2. Part-Time Jobs
Many students take on part-time jobs to supplement their allowances. These jobs can range from working in retail and restaurants to tutoring and freelance work. Part-time employment not only provides additional income but also valuable work experience.
3. Scholarships and Grants
Scholarships and grants are another significant source of money for students. These are usually awarded based on academic performance, sports, or other achievements. Unlike loans, scholarships and grants do not need to be repaid, making them a highly beneficial source of funding.
4. Student Loans
Student loans are a common way to finance higher education. While they provide the necessary funds to cover tuition and living expenses, it is important to understand the long-term implications of borrowing, including interest rates and repayment terms.
5. Freelancing and Gig Economy
With the rise of the gig economy, students have more opportunities to earn money through freelance work, such as writing, graphic design, and coding. Platforms like Upwork and Fiverr allow students to offer their services and earn money flexibly.
Principal Uses of Money
1. Basic Living Expenses
Money is primarily used to cover basic living expenses, including housing, food, transportation, and utilities. Managing these expenses effectively is crucial for maintaining a stable living situation.
2. Education-Related Costs
Tuition fees, textbooks, and other educational materials are significant expenses for students. Proper budgeting for these costs ensures that students can meet their academic requirements without financial stress.
3. Savings and Investments
Setting aside money for savings and investments is an essential aspect of good financial management. This practice helps in building a financial cushion for emergencies and future needs.
4. Leisure and Entertainment
While managing finances, it is also important to allocate money for leisure and entertainment. This balance ensures that students can enjoy their social lives and hobbies without overspending.
Mismanagement of Money
1. Impulse Spending
One of the most common forms of money mismanagement is impulse spending. This occurs when students make unplanned purchases without considering their budget or financial goals.
2. Accumulating Debt
Mismanagement of credit cards and loans can lead to significant debt. High-interest rates and late payment fees can quickly accumulate, creating a financial burden that can take years to resolve.
3. Lack of Budgeting
Without a clear budget, students may struggle to keep track of their income and expenses. This can result in overspending and an inability to save money for future needs.
4. Ignoring Savings
Failing to save money is another critical aspect of financial mismanagement. Without savings, students may find themselves unprepared for unexpected expenses or emergencies.
Consequences of Mismanagement of Money
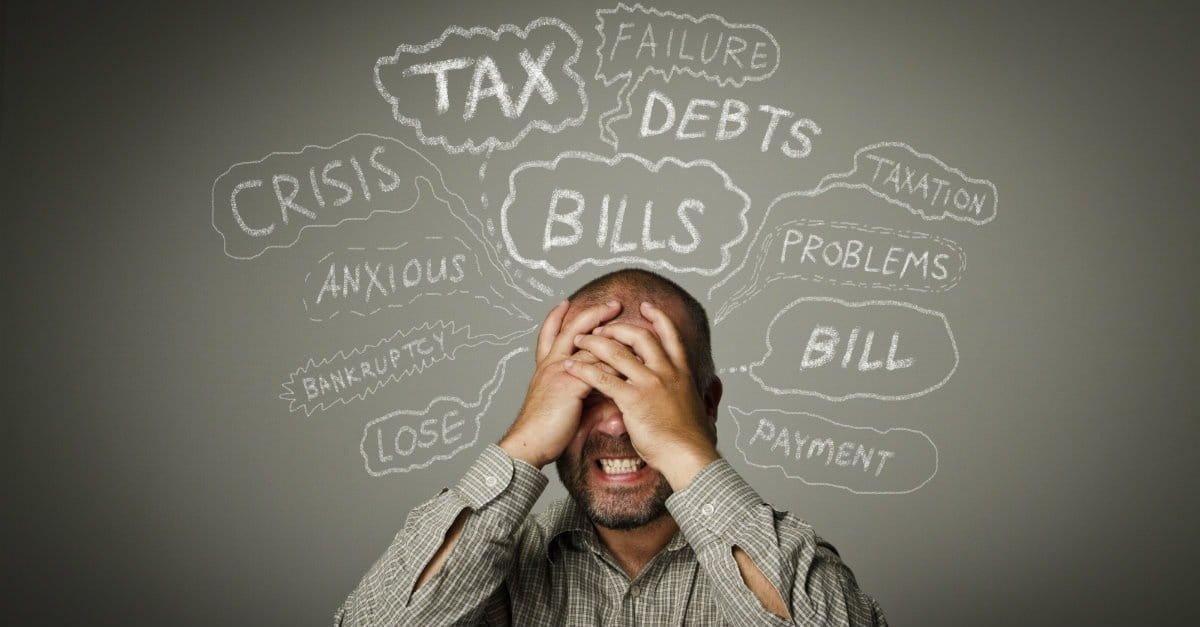

1. Financial Stress
Poor money management can lead to significant financial stress. Constantly worrying about how to pay bills or cover expenses can take a toll on a student's mental and emotional well-being.
2. Poor Academic Performance
Financial problems can distract students from their studies, leading to poor academic performance. The stress and time spent dealing with financial issues can reduce the focus and energy needed for academic success.
3. Damaged Credit Score
Mismanaging credit cards and loans can result in a damaged credit score. A low credit score can affect future borrowing ability, including getting approved for loans, renting apartments, and even some job opportunities.
4. Limited Opportunities
Financial instability can limit opportunities for internships, study abroad programs, and extracurricular activities that require additional funds. Missing out on these opportunities can impact a student's personal and professional development.
Good Management of Money
1. Budgeting
Creating a budget is the foundation of good money management. A budget helps students track their income and expenses, ensuring that they live within their means and allocate funds for essential needs.
2. Prioritizing Expenses
Students should prioritize their expenses based on necessity. Essential costs such as rent, utilities, and educational expenses should take precedence over discretionary spending.
3. Saving Regularly
Setting aside a portion of income for savings is crucial. Establishing a savings habit early on can help students build financial security and prepare for future goals and emergencies.
4. Smart Borrowing
When borrowing money, students should carefully consider the terms and conditions. Opting for low-interest loans and making timely repayments can prevent debt from becoming unmanageable.
5. Seeking Financial Advice
Students can benefit from seeking financial advice from trusted sources, such as financial advisors, family members, or educational resources. This guidance can help them make informed decisions about their finances.
The Importance of Saving
1. Financial Security
Savings provide a safety net for unexpected expenses, such as medical emergencies or sudden changes in living situations. Having savings ensures that students are not caught off guard by unforeseen financial challenges.
2. Achieving Goals
Saving money allows students to achieve their financial goals, whether it is purchasing a car, funding further education, or starting a business. Setting clear savings goals and working towards them provides a sense of accomplishment and financial independence.
3. Reducing Stress
Financial instability can cause significant stress and anxiety. By saving money and managing finances effectively, students can reduce financial stress and focus on their academic and personal growth.
4. Building Wealth
Starting to save and invest early can have a profound impact on long-term financial health. Compound interest and smart investments can help students build wealth over time, providing financial stability in the future.
Additionally
Effective money management is a vital skill that students must develop to ensure financial stability and success. By understanding the sources of money, its principal uses, the pitfalls of mismanagement, and the benefits of good management, students can make informed financial decisions. Saving money and prioritizing expenses are crucial practices that contribute to financial security and the achievement of long-term goals. By adopting these principles, students can pave the way for a financially secure and prosperous future.